Run configuration settings
Switching compilers
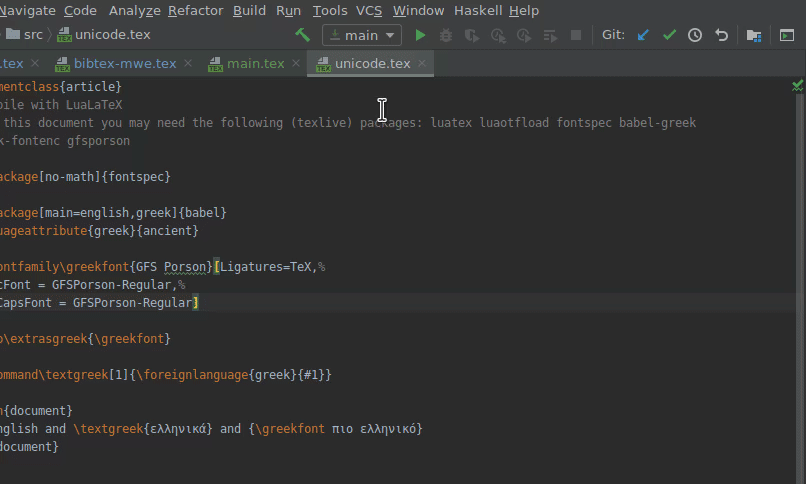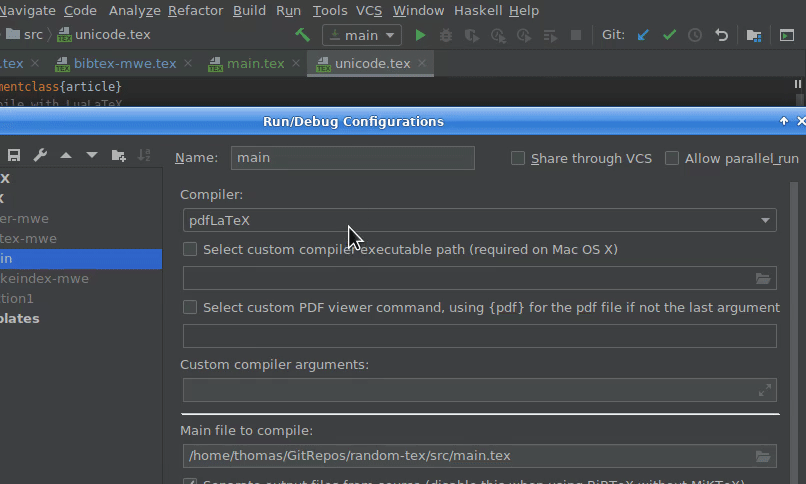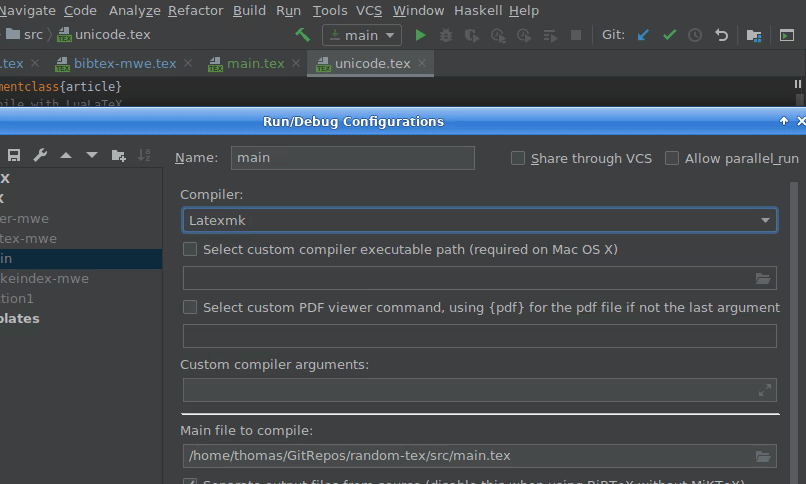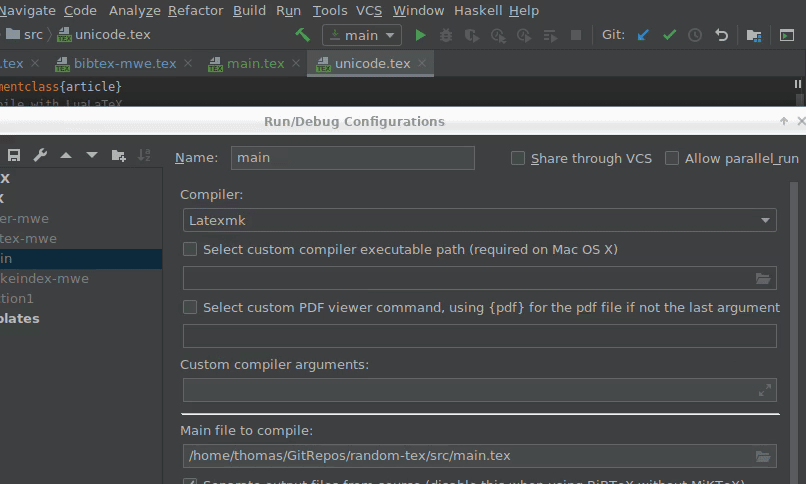
You can switch to a different compiler by clicking on the dropdown list next to the run button, select Edit Configurations and select a different compiler in the Compiler dropdown menu. Make sure you have it installed correctly.
Using magic comments to specify the compiler for new run configurations
To set the compiler of a document, put the magic comment
at the top of the root file. The syntax %! Program = is also supported.
To set the BibTeX compiler, put the magic comment
at the top of the LaTeX root file. An example for compiling with lualatex that needs --shell-escape and biber:
Note: These magic comments only take affect when creating a new run configuration (using Ctrl + Shift + F10 or using the gutter icon). They have no effect on already existing run configurations, which can be edited using Edit Configurations dialog.
LaTeX compilers
pdfLaTeX
pdfLaTeX is the default compiler for TeXiFy. It is the most simple compiler, but one which is very stable.
LuaLaTeX
To use LuaLaTeX, install the luatex package. When using custom fonts, use either LuaLaTeX or XeLaTeX. LuaLaTeX has the advantage that you can use Lua (a programming language) in your LaTeX.
Latexmk
See https://mg.readthedocs.io/latexmk.html for installation and more information. With TeX Live, install with tlmgr install latexmk. With Latexmk the project is compiled just as much times as needed and handles BibTeX/Biber. It uses pdflatex by default, but you can use an other compiler as well.
When you use a latexmkrc file (see the man page of latexmk for information) then TeXiFy will only add output-format, -auxil-directory and -output-directory command line arguments, because otherwise your options in your latexmkrc file would be overwritten. You can still of course add additional command line arguments in the run configuration, including the location of the latexmkrc file with the -r flag. If you want to tell TeXiFy to use the output format of your latexmkrc, make sure the DEFAULT output format is selected. TeXiFy will also read additions to the TEXINPUTS environment variable from your latexmkrc file, assuming you add it with the syntax like ensure_path('TEXINPUTS', 'subdir1//');.
Tip: compiling automatically when IntelliJ loses focus
When you add the flag -pvc it watches the files and recompiles automatically on saved changes (in IntelliJ a save is triggered, when the window looses focus, or by Ctrl +S).
For an automatic start of your pdf viewer you have to create a file in your users home directory. The path for the file is under Linux and Mac $HOME/.latexmkrc and under Windows %USERPROFILE%\.latexmkrc. In this file you need to add the following line:
The quotes are needed to handle whitespaces in the path properly.
XeLaTeX
To use XeLaTeX, install the xetex package. When using custom fonts, use either LuaLaTeX or XeLaTeX.
Texliveonfly
To use texliveonfly, install the texliveonfly package. The purpose of texliveonfly is to install TeX Live packages automatically during compilation of a document, like the on the fly installation of MiKTeX but then much slower. So it is only relevant if you have TeX Live, and if you do not have a full install with all the packages already installed. You can use texliveonfly with any other LaTeX compiler.
For more info have a look at https://tex.stackexchange.com/a/463842/98850
Tectonic
Since b0.6.6
See https://tectonic-typesetting.github.io/en-US/ for installation and more info. Tectonic has the advantage that it downloads packages automatically, compiles just as much times as needed and handles BibTeX, but it often only works for not too complicated LaTeX documents. It also has automatic compilation using tectonic -X watch.
There is some basic support for a Tectonic.toml file, including inspection support (missing imports, for example) for multiple inputs in the toml file (Tectonic 0.15.1 or later).
The documentation can be found at https://tectonic-typesetting.github.io/book/latest/
BibTeX compilers
For more information about the bibtex compilers, see the Bibtex page.
Custom compiler path
Select a path to a LaTeX compiler.
Custom compiler arguments
Extra arguments to pass to the compiler. It depends on the compiler which ones are there by default. For more info, check the implementation at https://github.com/Hannah-Sten/TeXiFy-IDEA/blob/master/src/nl/hannahsten/texifyidea/run/compiler/LatexCompiler.kt This field has autocompletion, where the available options depend on the compiler that was selected when you opened the dialog.
Environment variables
You can pass environment variables to the command that is run to compile the LaTeX file. There is an option to include system variables. You can use for example the TEXINPUTS environment variable to include LaTeX files in a different directory anywhere on your system. For example TEXINPUTS=/path/to/directory//:, where // means that LaTeX (and TeXiFy) will search in any subdirectory of /path/to/directory for the file to be included, and : means to include the standard content of TEXINPUTS. For Windows, it is similar: TEXINPUTS=C:...\path\to\directory\; (note the semicolon). Similarly, you can also set TEXMFHOME to some other path than the default ~/texmf, so that sty and cls files will be searched in the tex/latex subdirectory or any child directory of it. For more information about paths resolving, see https://www.tug.org/texinfohtml/kpathsea.html#Path-searching
Expand macros in environment variables
Since b0.10.1
When ticked, macros such as $ContentRoot$ (the path to the content root of the current run configuration's main file) are expanded. An example use for this would be to add a directory containing the document class to be used to TEXINPUTS, e.g., TEXINPUTS=$ContentRoot$/MyDir. Doing so might be especially helpful in the context of setting up a 'run configuration template,' which is a run configuration that is used by default for any time a LaTeX file is run (and thus compiled) for the first time. For more details on run configuration templates, see https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/run-debug-configuration.html#templates.
An overview of all built-in macros can be found at https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/built-in-macros.html. Whenever the documentation mentions 'the current file,' in the context of a TeXiFy run configuration, this always refers to the main .tex file being compiled.
LaTeX code to run before compiling the main file
Since b0.9.5
You can enter LaTeX code to be executed before the main file. For example, suppose you want to have two versions of a document, then you could create two run configurations and use this field to set a boolean flag to a different value.
For example, if your LaTeX file contains
then you can put \newcommand{\waarde}{false} in this field in your run configuration to set the value of the boolean to false. This works for at least pdflatex, lualatex, xelatex and latexmk.
Choose pdf viewer
Since b0.7.2
This lists all supported pdf viewers that are installed on your system, which you can select as the default pdf viewer. Selecting a supported viewer as default means that you get forward and inverse search, and that the selected pdf viewer is the viewer that will open when compilation is done.
The supported pdf viewers are the internal PDF viewer on all platforms, Sumatra for Windows, and Evince, Okular, and Zathura for linux, or no pdf viewer at all. For Mac/Linux, you can also select System default, which will just run open/xdg-open, without forward search. You can use any other pdf viewer by selecting the option Custom PDF Viewer.
Allow PDF viewer to focus after compilation
In general, TeXiFy will try to forward search to the pdf viewer after compilation. Depending on the pdf viewer, this may transfer focus away from the IDE. If you do not want this, you can deselect this option.
At the moment, the behaviour is:
Evince: will forward search and focus when this option is selected, will not forward search otherwise
Okular: will always forward search and never focus
Skim: will always forward search, will focus depending on the option
Zathura: will always forward search and focus
SumatraPDF: will always forward search, will focus depending on the option
PDF Viewer Plugin: will always forward search and never focus
Custom pdf viewer
In the Custom pdf viewer field you can specify the command for your favourite pdf viewer, so for example if the command is okular somefile.pdf then you can fill in okular here. If the pdf file is not the last argument, you can use the {pdf} placeholder, so okular {pdf}.
Then when you run the run configuration, when the compilation has finished the pdf will open in the viewer you specified.
If you don’t want to open any pdf viewer for some reason, select the checkbox but leave the field empty.
Choose LaTeX source file to compile
Select a LaTeX file.
Set a custom path for auxiliary files
When using MiKTeX, this path will be passed to the -aux-directory flag for pdflatex, and similar for other compilers which support an auxiliary directory.
By default, TeXiFy will put output files (pdf) in an out directory, and auxiliary files (aux, log, etc.) in an auxil directory to keep your project clean. However, there are some special cases. Note that using latexmk is also a great way to keep your project clean as it will not keep the intermediate files at all, but it requires Perl to be installed.
Bibtex and TeX Live
When using TeX Live and bibtex, using the auxil directory will not work for bibtex as it will not be able to find the source bib file. TeXiFy detects when you are using bibtex to generate a bibtex run configuration. When doing so, it will set the working directory of the bibtex run configuration to the auxil directory, and update the BIBINPUTS environment variable so that everything should work as you would expect.
Makeindex
TeXiFy will generate a Makeindex run configuration when it detects you are using an index. However, generated index files like .ind need to be next to the main file otherwise these index packages won’t work, so TeXiFy will, after running the index program in the auxil directory, temporarily copy these files to the right place and clean them up afterwards (similar, though perhaps less efficient, to what latexmk would do). For bib2gls, which needs the bib file, we copy the auxil file and run bib2gls next to the main file instead.
Minted
Minted needs to find its own generated .pyg file in the auxil directory, if you use it. You can tell this to minted by using \usepackage[outputdir=../auxil]{minted}.
Set a custom path for output files
This path will be passed to the -output-directory for pdflatex, and similar for other compilers which support an output directory.
If you are using pdflatex and bibtex under TeX Live, when your output directory is set to something different than the directory of your main file, then you need to provide the BIBINPUTS environment variable in the bibtex run configuration. This should point to the directory your main file is in, e.g. BIBINPUTS=../src. TeXiFy will automatically do this for you if you create a run configuration from context (for example using the gutter icon next to \begin{document}). The exception to this is when you have changed your openout_any setting in TeX Live.
Since b0.7.1 You can use the {mainFileParent} and {projectDir} placeholders here, which will be resolved when you run the run configuration. The first one resolves to the directory your main file is in, the second to the content root of the main file. These placeholders are especially useful in template run configurations, so you can specify paths relative to these directories in the template run configuration, when the main file is not yet known. If you enter for example {mainFileParent}/out, then the out directory will always be created next to the main file when new run configurations are created.
Always compile twice
When enabled, TeXiFy will always compile at least twice. Can be useful to make sure your references are always updated.
Choose output format
Some compilers support different output formats than just pdf, for example dvi.
Choose LaTeX distribution
When a different LaTeX distribution is detected, like Dockerized MiKTeX or TeX Live from WSL, you can choose it here. Note that you can also change this in the run configuration template to always use a different LaTeX distribution.
Dockerized MiKTeX
When you have no TeX Live or MiKTeX installed directly on your system, but you do have a miktex docker image downloaded (it checks for 'miktex' in the output of docker image ls, TeXiFy assumes you want to use Dockerized MiKTeX. You can also turn it on in the run configuration settings or template to always use Dockerized MiKTeX even if you have other LaTeX distributions installed.
Since the official Dockerized MiKTeX image at https://hub.docker.com/r/miktex/miktex is a bit old, which can cause problems downloading new packages, we provide our own Dockerized MiKTeX via GitHub. You can pull it with docker pull ghcr.io/hannah-sten/texify-idea/miktex:latest.
You can then run your favourite LaTeX compiler like usual, and TeXify will make sure to perform the docker run (you can see the exact command at the top of the output log). Custom output directories are supported.
Installation of Docker
To install Docker, see https://docs.docker.com/install/, for example use your package manager.
Make sure to start the
dockerservice (and enable if you want to start it on boot)To avoid a permission denied error when running, add yourself to the
dockergroup.Reboot (logging out and in may not be enough)
You have to login to GitHub to use the Docker image: get a github token from https://github.com/settings/tokens, save it somewhere secure and run
echo my_token | docker login https://docker.pkg.github.com -u myusername --password-stdinSee https://help.github.com/en/packages/using-github-packages-with-your-projects-ecosystem/configuring-docker-for-use-with-github-packages#authenticating-to-github-packages for more info.
Advanced Docker setups
TeXiFy provides a very limited interface to Docker: you can select images and configure the path to your docker executable, but most is hardcoded. For more advanced Docker configuration, we recommend to use the Docker plugin. As a starting point, you can have a look at the command that TeXiFy runs if you select Docker in the run configuration, it will be at the top of the console output window. You can create a Docker run configuration to run a TeX Live or MiKTeX docker container. Then you can use any Docker flags or other features like podman support.
Dockerized TeX Live
Similar to the MiKTeX docker image, you can also use a texlive docker image if you have it installed. By default, the official texlive/texlive image is used. If you use IntelliJ, you can select a different image name by creating a LaTeX Docker SDK, see Project configuration.
TeX Live from WSL
Since b0.6.10
In the Run configuration settings you can choose to use TeX Live from WSL.
Setup
Install WSL, see for example https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10
Install TeX Live as usual, see for example TeX Live installation.
Add
export PATH="/path/to/texlive/yyyy/bin/x86_64-linux:$PATH"to your~/.bashrc.
Currently, TeXiFy will use bash to run LaTeX compilers. Test your installation with bash -ic "pdflatex --version".
Troubleshooting
If pdflatex is not found, double check if the default wsl distribution is the one in which you installed LaTeX with wsl -l
Choose External LaTeX tool run configuration
You can add BibTeX, Makeindex or other external tool run configurations to your main LaTeX run configuration. They will be run appropriately inbetween LaTeX runs.
Other tasks to run before the run configuration, including other run configurations or external tools
Use this to run anything before the run configuration. See https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/run-debug-configurations-dialog.html#before-launch-options